I. What Is A Press Brake
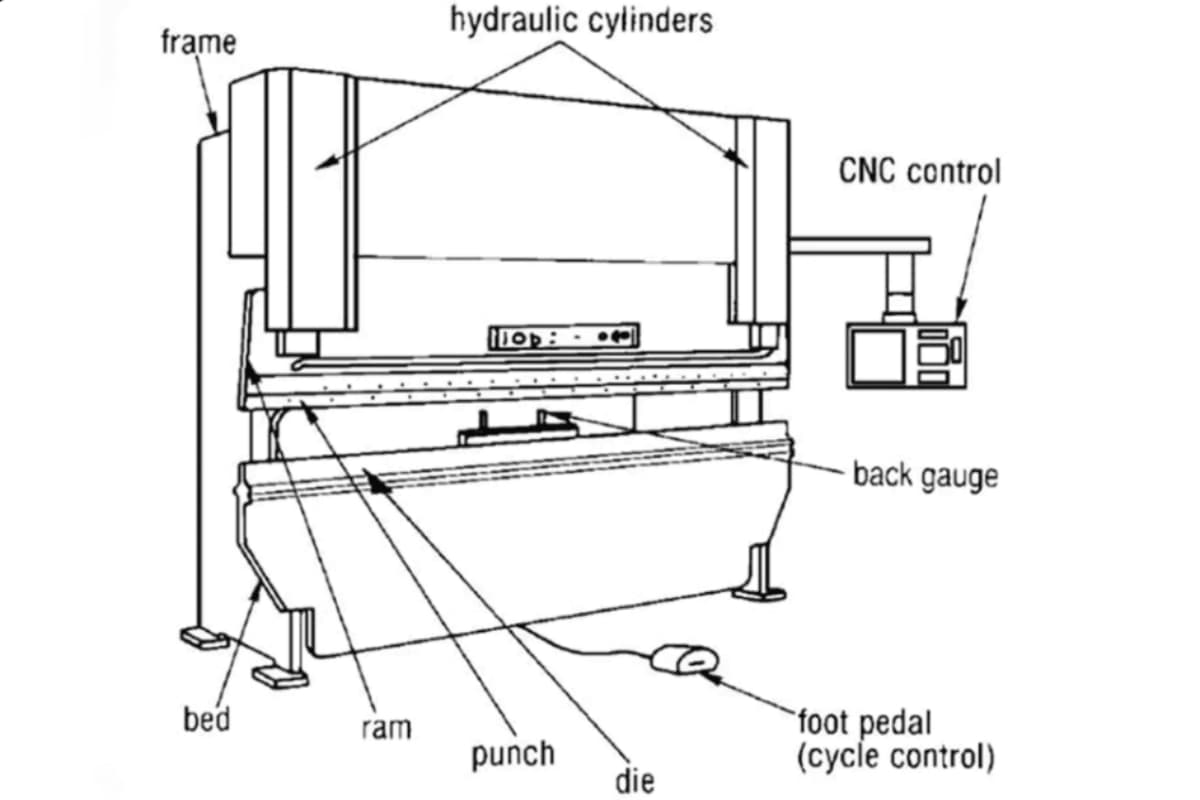
Press brake is a versatile machine tool used in industries and fabrication shops for bending sheet metal to a desired angle and shape. The sheet metal bending process is accomplished by applying force on the point of the bend. The metal sheet is placed between the punch and the die on the press brake machine. The punch is the upper component, and the die is the lower component.
The press brake machine exerts force on the metal sheet through the punch, causing it to bend or deform according to the shape of the die. As the punch forces the metal into the die, the material bends. The force applied by the punch, and hence the bending, can be mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, or servo-electric, each having a specific use-case and advantages.
It drives punches and dies through different driven sources to bend repeatable sheet metal and form profiles. Materials of different thicknesses and lengths require different bending forces. Simply put, press brake forming is a process used to bend and shape sheet metal.
Bending force, measured in tonnage, is the force exerted by the press brake. Tonnage determines the press brake’s load limit. If a press brake has a higher tonnage, it can bend thicker and longer sheet metal. Different types of press brakes produce tonnage in different ways. The hydraulic press brake machine is suitable for bending with large tonnage, while driven sources are generally divided into mechanical, hydraulic, electric, and pneumatic types.
The name of the press brake is determined by the driving method. For example, the pneumatic bending machine drives the ram through air pressure, while the servo-electric press brake drives the ram using a servo motor. The servo-electric press brake offers very high precision and speed.
II. How does A Press Brake Work
Modern common type of press brakes can be mainly divided into mechanical and hydraulic press brakes. At present, the modern press brake has developed into the advanced Computer Numerical Control (CNC) hydraulic press brake. Using CNC press brake can handle all kinds of complex and mass workpiece-forming tasks.
Here is a detailed comparison of different types of press brakes (hydraulic, mechanical, CNC) along with their respective advantages and disadvantages:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Hydraulic Press Brake | High precision and control Suitable for various materials and thicknesses Capable of handling heavy materials Even force distribution | High cost Complex operation Cannot exceed rated tonnage |
| Mechanical Press Brake | High precision and consistency Suitable for thin to medium-thickness materials Quick setup and tool change Ideal for forming complex shapes | Requires frequent tool changes and setups May lock into a complete cycle Requires skilled operation |
| CNC Press Brake | High precision and automation Easy to operate, reduces labor intensity Suitable for various shapes and angles Increases production speed and efficiency Programmable, suitable for multi-step operations | High cost Limitations with highly reflective or brittle materials Requires specialized training and maintenance |

The mechanical press brake drives the flywheel through the motor. The operator operates the clutch to control the flywheel, and the crank drives the movement of other parts. The operation of a press brake is relatively simple, and it can handle large tonnage bending.
The hydraulic press brake is driven by the synchronous movement of the hydraulic cylinder. There is a hydraulic cylinder on each side of the uprights, and the hydraulic cylinder is connected to the ram through the piston rod.
The movement of the hydraulic cylinder drives the ram up and down. The movement modes of the hydraulic press brake are divided into up-moving and down-moving. The back gauges accurately position the workpiece through the movement of different axes. The hydraulic press brake has the advantages of high speed and high precision. However, the tonnage of bending is limited, which is a disadvantage.

The CNC press brake is a hydraulic press brake equipped with a CNC control system that controls the movement of each part with modular programming functions and high precision. The operator can set parameters through the control system. For example, bending angle, plate thickness, flange length, cycle time, stress, etc.
Additionally, the CNC press brake is also equipped with an automatic feeding system that accurately controls the position of the workpiece through the movement of the ram and back gauge. Synchronous movement of the motor drive axes of the back gauge and the ball screws. The back gauge can accurately measure the length of the flange being formed.
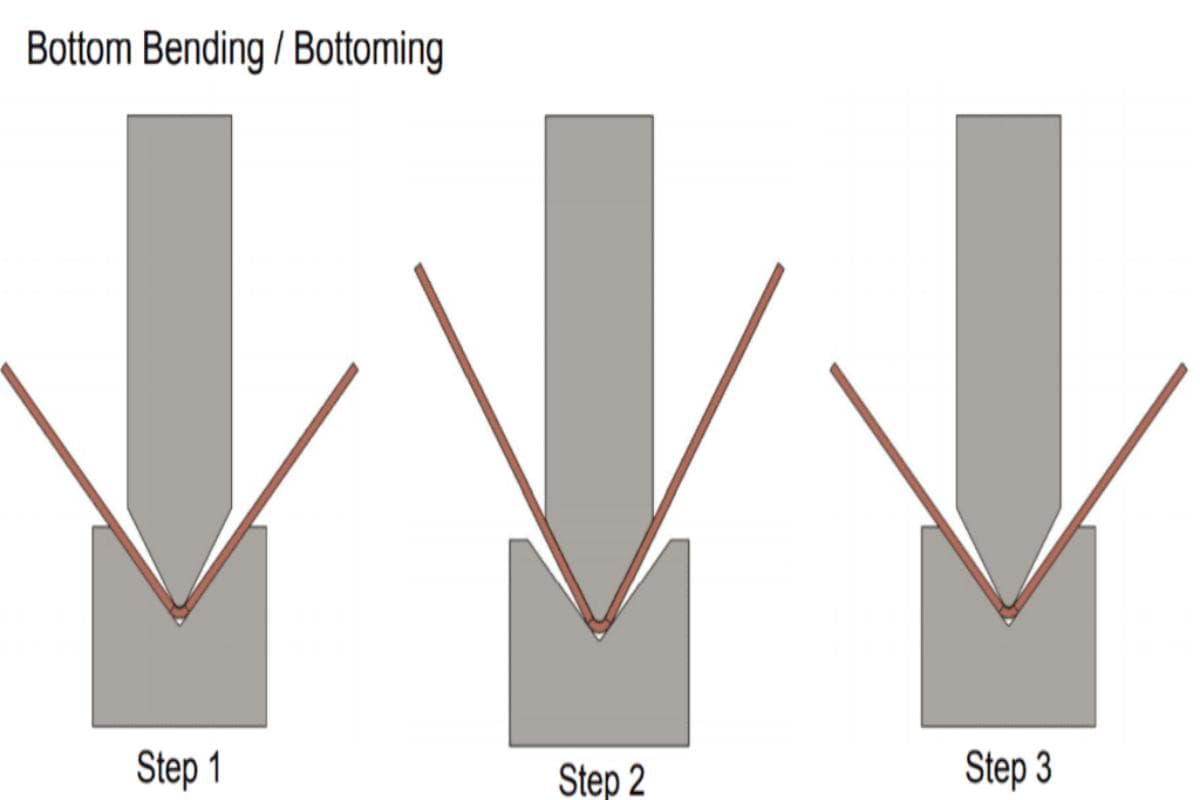
Adjust the bending angle by adjusting the ram movement through the control system. There are basically three bending methods: air bending, bottom bending, and embossing bending. The choice of bending method has a great relationship with the thickness of the plate.
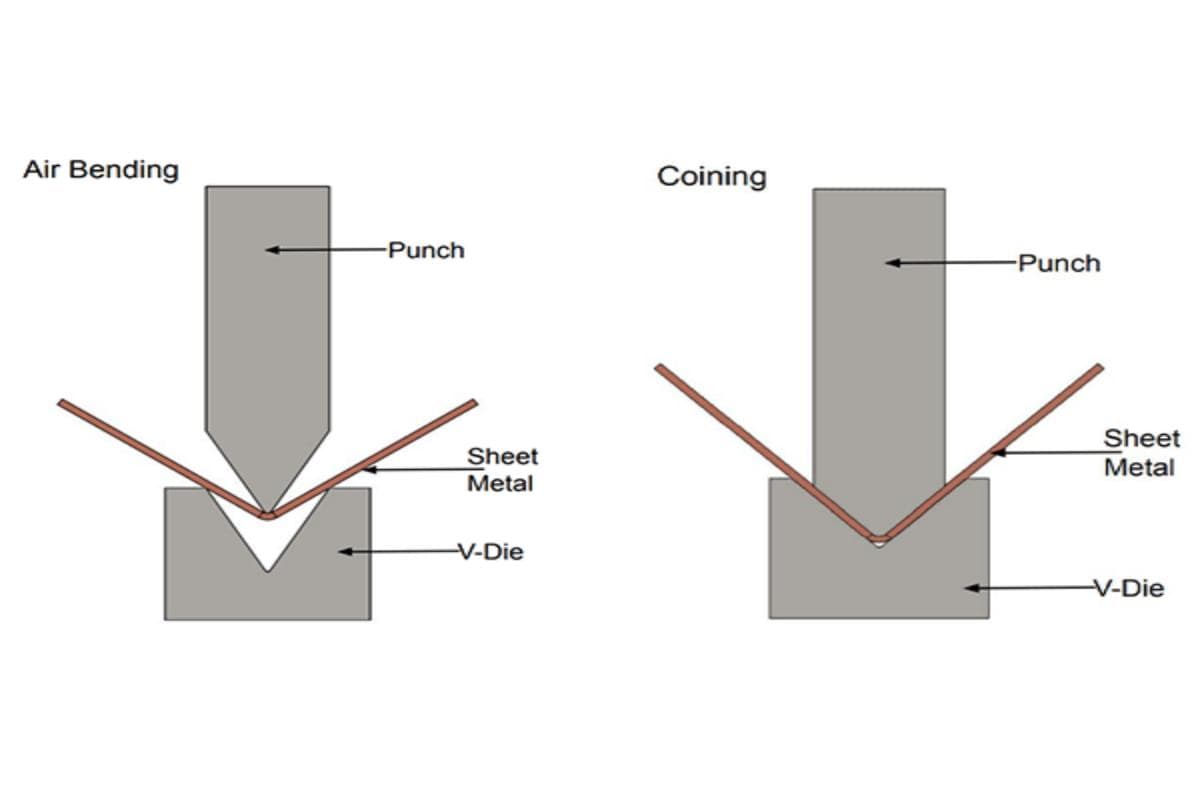
Air bending is the most commonly used bending method, where the workpiece is not in full contact with the bottom die. It can be carried out with relatively small tonnage. Bottom bending and coining methods can also be used as needed.
During bending, the hydraulic cylinders drive the movement of the ram, which in turn drives the upper die to apply pressure on the lower die on the workbench. The sheet metal in the middle is formed into a specific angle through the extrusion of the die, and after repeated bending, the final profile is obtained.
The angle and shape of the metal plate are determined by the shape of the punches and dies, as well as the movement of the ram. The CNC press brake offers flexible numerical control and programming functions, making it operator-friendly.
III. How to set up a press brake?
First of all, it is critical to understand the drawing of the bending workpiece. Determine the material, length, and thickness of the workpiece, as well as the bending angle, bending radius, flange dimension, and tolerance of the workpiece. Secondly, choose the appropriate bending method and die.
Select the appropriate bending method based on the relationship between the bending radius and metal thickness, such as air bending, bottom bending, or coining. Choose a punch and die set that match the material of the bending workpiece. Thirdly, determine the tonnage according to the tonnage table.
Consult the corresponding tonnage estimation provided by the manufacturer. If it is air bending, you can refer to the tonnage chart to determine the tonnage. The tonnage of bottom bending is four to six times that of air bending, and the tonnage of coining is eight to ten times that of air bending tonnage.
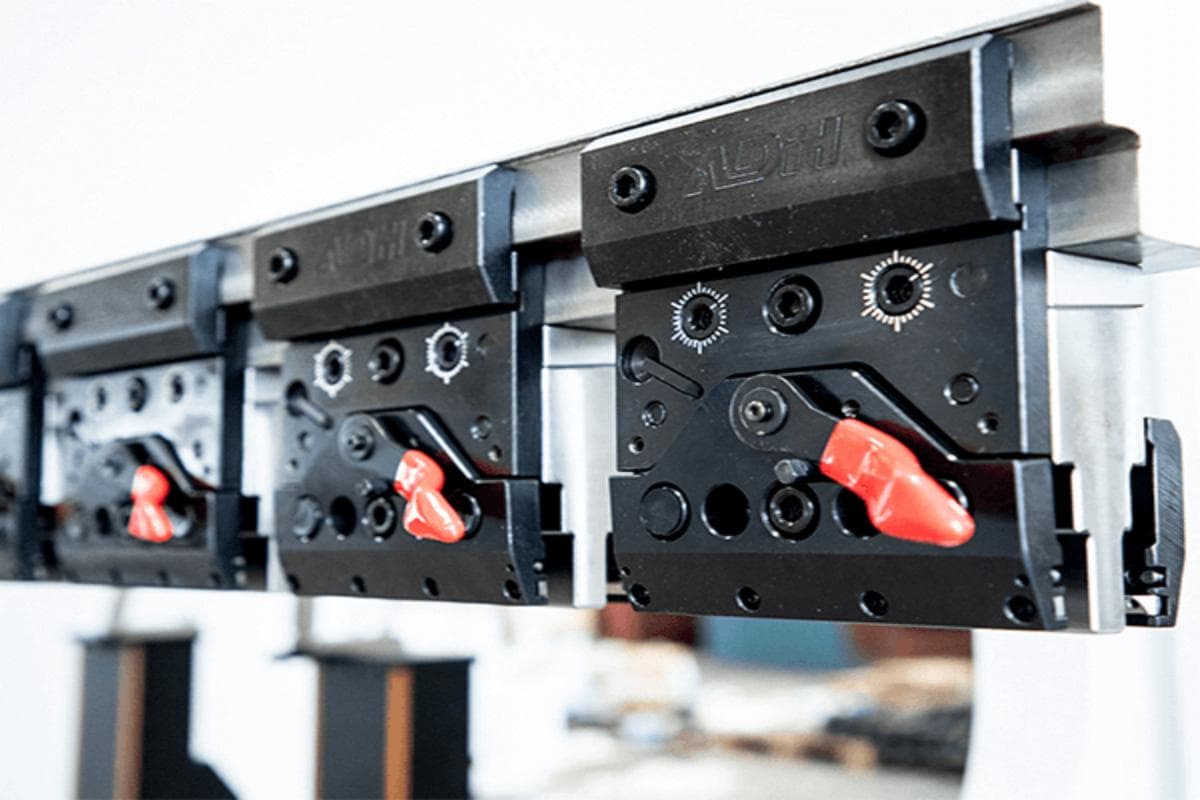

Press brake tooling plays a crucial role in achieving precise bends. Install and adjust the press brake tooling, including checking the thickness and proportion of the upper and lower dies, adjusting the stroke of the ram, adjusting the upper limit point of the toolings to reserve the stay position of the ram, and setting an appropriate gap between the upper and lower dies.
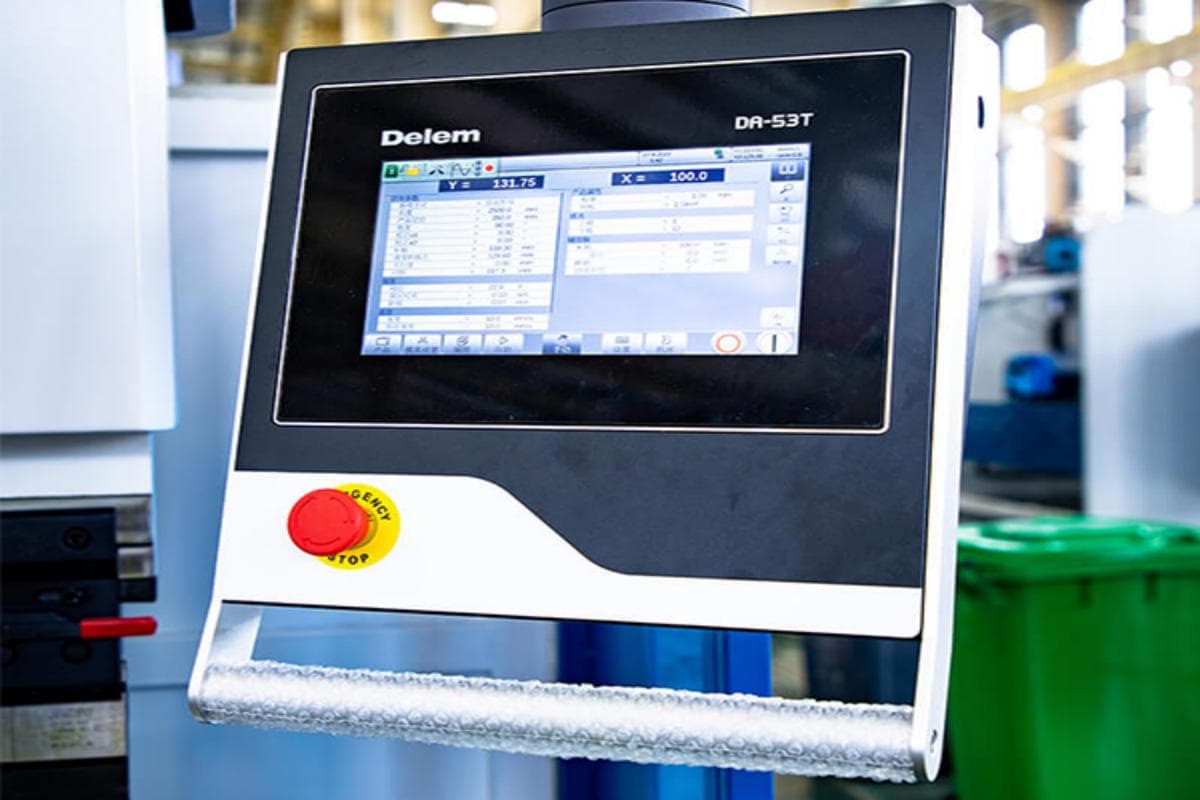

Perform the program procedure of the press brake, familiarizing yourself with the functions of the CNC controller, programming offline, and using scrap plates for a bending test. If there is a problem with the bent workpiece, check and correct the program, and operate the press brake accordingly. These steps can save costs and improve efficiency.
IV. Cases and Application
1. Automotive Industry
Press brakes are widely used in the automotive industry to manufacture various car components such as brackets, chassis, body panels, and exhaust systems. Their high precision and consistency ensure the quality and safety of these parts. For example, press brakes can accurately bend metal sheets to meet the stringent specifications of car manufacturers, resulting in high-quality vehicles.
2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, press brakes are used to produce critical components like aircraft frames, wing parts, and engine covers. Given the need for extreme precision and reliability in aerospace parts, press brakes ensure the structural integrity and functionality of these components. For instance, press brakes can precisely bend aluminum and titanium alloys to meet the rigorous requirements of aircraft and satellites.
3. Home Appliance Industry
Press brakes are used in the home appliance industry to produce refrigerator panels, washing machine housings, and air conditioner components. Their high precision and flexibility allow manufacturers to meet the specific design requirements of each appliance. For example, press brakes can accurately bend metal sheets to produce appliance housings and internal components that adhere to design specifications.
4. Construction Industry
In the construction industry, press brakes are used to manufacture structural components, beams, and other metal elements used in building and infrastructure projects. For example, press brakes can bend metal sheets to produce structural components like I-beams and metal decking that meet architectural design requirements.
5. Furniture Manufacturing
Press brakes are used in furniture manufacturing to produce metal frames, brackets, and decorative metal parts. For example, press brakes can bend metal sheets to create complex shapes and angles that meet furniture design requirements, enhancing both the aesthetics and functionality of the furniture.
6. Medical Equipment
In the medical equipment manufacturing industry, press brakes are used to produce high-precision and high-performance metal components. For example, press brakes can bend metal sheets to produce components that meet the stringent specifications of medical devices, improving production efficiency and product quality.
7. Electronics and Electrical Equipment
Press brakes are used in the electronics and electrical equipment manufacturing industry to produce precise metal housings and components. For example, press brakes can bend metal sheets to create housings and brackets that meet the design requirements of electronic devices, ensuring their functionality and safety.
8. Defense Industry
In the defense industry, press brakes are used to manufacture high-strength metal plates and alloy components such as ammunition storage containers, armored vehicles, and armor plates. For example, press brakes can bend metal sheets to produce components that meet the stringent requirements of military equipment, enhancing the durability and safety of the equipment.
V. Common Faults of Press Brakes and Solutions

| Fault Phenomenon | Possible Causes | Solutions |
| No pressure or insufficient pressure in the hydraulic system | 1. Incorrect forward or reverse rotation of motor and pump 2. Blocked spool of overflow valve 3. Blocked spool of solenoid valve 4. Internal leakage of pressure control valve | 1. Check the rotation direction of motor and pump 2. Clean the spool of overflow valve 3. Clean the spool of solenoid valve 4. Check the pressure control valve |
| Slow or jerky descent of ram | 1. Worn or damaged cylinder 2. Worn or non-vertical guide rails 3. Low oil level in tank 4. Fast forward speed, insufficient oil supply 5. Stuck and not fully open filling valve | 1. Check the cylinder 2. Check the guide rails 3. Check the oil level 4. Adjust the fast forward speed 5. Clean the filling valve |
| Oil leakage in the hydraulic system | 1. Loose connecting screws and pipe fittings 2. Damaged seals | 1. Tighten screws and fittings 2. Replace seals |
| Unbalanced bending on both sides | 1. Uneven wear of dies 2. Non-parallel ram | 1. Adjust the hexagonal tube to correct the angle difference 2. Adjust the parallelism with eccentric sleeves |
| Loud noise | Loose connections, worn bearings, damaged parts | Adjust the ram, replace dies if necessary |
| Electrical faults | Loose wiring, sensor failure, damaged circuits | Check wiring, replace sensors or circuits |
| Overheating | Blocked radiator, cooling system failure | Clean the radiator, repair the cooling system |
| Ram cannot descend slowly, weak bending force | 1. Failure of 4/2-way valve 2. Stuck filling valve | 1. Check the 4/2-way valve 2. Clean the filling valve |
| Slow return speed of ram, high return pressure | Filling valve not open | Check the filling valve |
VI. Conclusion
There are many kinds of press brakes, such as mechanical press brakes, CNC press brakes, hydraulic press brakes, etc. No matter how advanced the technology of the press brake is, its basic working principle is similar. The modern CNC press brake is more advanced than the previous press brake technology, and the bending accuracy and efficiency have been greatly improved.
ADH produces various CNC press brakes, NC press brakes and large press brakes. You can consult our product experts to learn more about our press brake or other machines.
RBA Indexable Roughing Boring Head
RBA Indexable Roughing Boring Head
RBA Indexable Roughing Boring Head,RBA20 Indexable Roughing Boring Head,RBA32 Indexable Roughing Boring Head,RBA40 Indexable Roughing Boring Head
SICHUAN JOJO TOOLS CO., LTD , https://www.jojo-tools.com